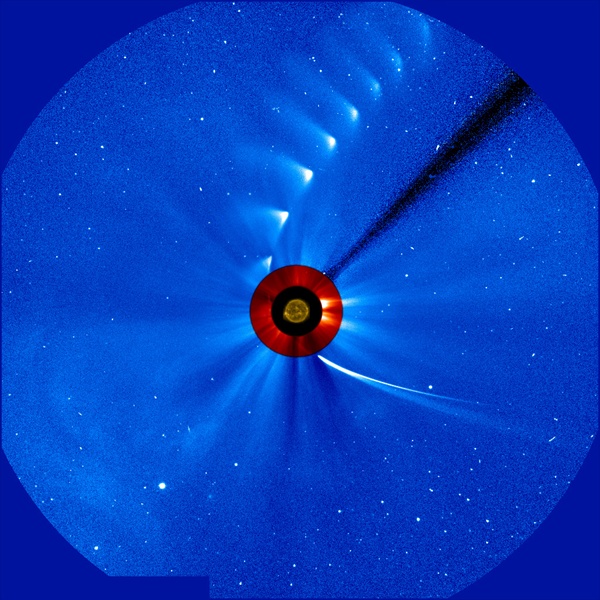
Comet ISON comes in from the bottom right and moves out toward the upper right, getting fainter and fainter, in this time-lapse image from the ESA/NASA Solar and Heliospheric Observatory. The image of the sun at the center is from NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory. ESA/NASA/SOHO/SDO/GSFC
From our January newsletter, By Dr Jenny Morris
2 December: Our star apparently destroyed this surprisingly fragile celestial visitor during their close encounter.
Comet ISON survived for more than 4.5 billion years in the frigid depths of the solar system, but it fizzled during its brief moment in the Sun on 28 November. Through a combination of ISON’s delicate makeup, the Sun’s intense heat, and — most importantly — our star’s powerful tidal forces, the comet’s nucleus failed to survive its brush within 730,000 miles (1.16 million kilometers) of the Sun’s surface.
As the comet approached perihelion (its least distance from the Sun), it continued to brighten at roughly the rate astronomers had predicted. Images from coronagraphs aboard both the Solar and Heliospheric Observatory (SOHO) and the Solar Terrestrial Relations Observatory (STEREO) showed the comet as a bright point of light trailed by one distinct dust tail and a narrow dust streamer.
However, ISON started to fade even before its closest approach to the Sun. The Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO), which is equipped with the best cameras for close-up observations of our star and its surroundings, failed to see the comet at perihelion. And once ISON had moved far enough beyond the Sun that it could reappear in SOHO’s coronagraphs, it was nowhere to be found.
As astronomers began to write their post-mortems, however, the unpredictable comet rose from the dead like the legendary Phoenix. Some 24 hours after perihelion, SOHO once again captured images of ISON showing a thin dusty tail and a diffuse central condensation that some interpreted as a small remnant of the comet’s nucleus. However, the revival soon began to peter out and by late on 29 November, the glow had faded to around 6th magnitude. Most scientists think the nucleus has dissipated, and any remaining dust likely will be too faint to see through anything but large telescopes. Even though ISON’s saga seems over, astronomers will spend months poring over their observations of this unique visitor.
By: Richard Talcott
To download our complete newsletter, click here…